Prepare for Dental Implants with Bone Grafting
At Maring Surgical Oral Surgery and Dental Implant Center in downtown Seattle, our oral surgeon is dedicated to providing comprehensive care that goes beyond the surface. We understand that a strong, healthy jawbone is the foundation for optimal oral health, a youthful appearance, and the long-term success of dental implants.
If you’re experiencing jawbone loss due to tooth extractions, periodontal disease, or other factors, our experienced oral surgeon and periodontist can help restore your bone structure and density through state-of-the-art bone grafting procedures. With our collaborative approach and dual-trained doctors, we’re uniquely positioned to deliver exceptional results and transform your oral health.
Call our Seattle oral surgeon at 206-343-7500 to schedule your consultation for bone grafting treatment. We proudly welcome patients, old and new, from our surrounding communities, including Mercer Island, Bellevue, and Kirkland.
Advanced Oral Care for Complex Cases in Seattle

Patients from Bellevue, Kirkland, Mercer Island, and Medina choose Maring Surgical when their dental needs exceed what can be safely handled in a general practice setting. Whether it’s bone grafting, a challenging tooth extraction requiring surgical expertise, comprehensive All-on-4® implant placement, or periodontal surgery that demands specialized training, our team provides the advanced care your referring dentist may not be able to perform in their office.
Dr. Thomas and Dr. Susan Maring’s unique combination of dental and medical training, along with our state-of-the-art downtown Seattle facility, makes us the trusted choice for complex oral surgical procedures throughout the greater Seattle area. We work closely with your dentist to ensure coordinated care from consultation through recovery.
What Is Bone Grafting?
Bone grafting is a surgical procedure that involves transplanting bone tissue to the jawbone to rebuild its structure and density. This can be done using the patient’s own bone, donor bone, or synthetic bone substitutes. By replenishing the jawbone, we can:
- Improve the stability and health of existing teeth
- Provide a strong foundation for dental implants
- Enhance the appearance of the face by supporting facial muscles
- Prevent further bone loss and the complications that can arise from it
Types of Bone Grafts
Autogenous Grafts
Autogenous bone grafts, also known as autografts, are made from your own bone and taken from somewhere else in the body. The bone is typically harvested from the chin, jaw, lower leg bone, hip, or skull. Autogenous bone grafts are advantageous in that the graft material is live bone, meaning it contains living cellular elements that enhance bone growth.
Allogenic Grafts
Allogenic bone, or allograft, is dead bone harvested from a cadaver that is then processed. Unlike autogenous bone, allogenic bone cannot produce new bone on its own. Rather, it serves as a framework or scaffold over which bone from the surrounding bony walls can grow to fill the defect or void.
Xenogenic Grafts
Xenogenic bone is derived from the non-living bone of another species, usually a cow. The bone is processed at very high temperatures to avoid the potential for immune rejection and contamination. Like allogenic grafts, xenogenic grafts serve as a framework for bone from the surrounding area to grow and fill the void.
Both allogenic and xenogenic bone grafting are advantageous in that they do not require a second procedure to harvest your own bone, as with autografts.
Synthetic Bone Grafts
As a substitute for using real bone, many synthetic materials are available as a safe and proven alternative, including:
- Demineralized Bone Matrix (DBM)/Demineralized Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft (DFDBA): This product is processed allograft bone, containing collagen, proteins, and growth factors that are extracted from the allograft bone. It is available in the form of powder, putty, chips, or a gel that can be injected through a syringe.
- Graft Composites: Graft composites consist of other bone graft materials and growth factors to achieve the benefits of a variety of substances. Some combinations may include a collagen/ceramic composite, which closely resembles the composition of natural bone; DBM combined with bone marrow cells, which aids in the growth of new bone; or a collagen/ceramic/autograft composite.
- Bone Morphogenetic Proteins: Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) are proteins naturally produced in the body that promote and regulate bone formation and healing.
Synthetic materials also have the advantage of not requiring a second procedure to harvest bone, reducing risk and pain. Each bone grafting option has its own risks and benefits. Dr. Thomas Maring will determine which type of bone graft material is right for you.
The type of graft used will depend on your individual needs and preferences, as well as the specific areas of bone loss. Our oral surgeon will work closely with you to develop a personalized treatment plan.
Causes of Oral Bone Loss
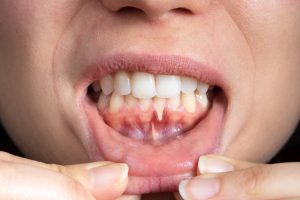 There are several common reasons why patients may experience jawbone loss:
There are several common reasons why patients may experience jawbone loss:
- Tooth extraction or tooth loss: When a tooth is lost, the surrounding bone begins to deteriorate.
- Periodontal (gum) disease: This progressive infection can destroy the bone that supports the teeth.
- Facial trauma: Injuries to the jaw can damage the underlying bone structure.
- Congenital conditions: Some people are born with abnormalities that affect jaw development and bone density.
- Tumors or cysts: Growths in the jaw can compromise the bone over time.
Benefits of Bone Grafting
By restoring lost bone volume and density through grafting, our patients enjoy a wide range of benefits:
- Improved oral health and function
- Enhanced facial aesthetics by supporting the lips and cheeks
- Increased success rate for dental implants
- Prevention of further bone loss and dental complications
- Restored confidence in their smile and oral function
The Bone Grafting Process at Maring Surgical
 Dental bone grafting is typically performed in multiple stages to ensure the best possible outcome. Here’s what you can expect:
Dental bone grafting is typically performed in multiple stages to ensure the best possible outcome. Here’s what you can expect:
- Consultation: Our Seattle oral surgeon will evaluate your oral health and determine if bone grafting is the right treatment option for you.
- Preparation: The treatment area is carefully prepared, and you’ll receive a local anesthetic and any necessary sedation.
- Graft Placement: The bone graft material is meticulously placed in the areas of bone loss, and the site is secured with sutures.
- Healing: You’ll receive detailed aftercare instructions to promote proper healing and integration of the new bone.
Bone Grafting for Dental Implants
If you’re considering dental implants, bone grafting is often a crucial first step. Implants require a strong, dense jawbone to be successfully placed and integrated. By rebuilding the bone structure via ridge augmentation, we can ensure your implants have the solid foundation they need for long-term stability and function. Sometimes, patients do not have the upper jawbone to support dental implants, or their sinus cavity is too close to where the implant site would be. Dr. Maring can perform a sinus lift to create a sturdy foundation and prevent your sinuses from being affected by your dental implants.
Our team at Maring Surgical Oral Surgery and Dental Implant Center works closely with patients to assess their candidacy for dental implant surgery and determine if bone grafting is necessary. We’ll develop a comprehensive treatment plan to get you on the path to a beautiful, fully functional smile.









